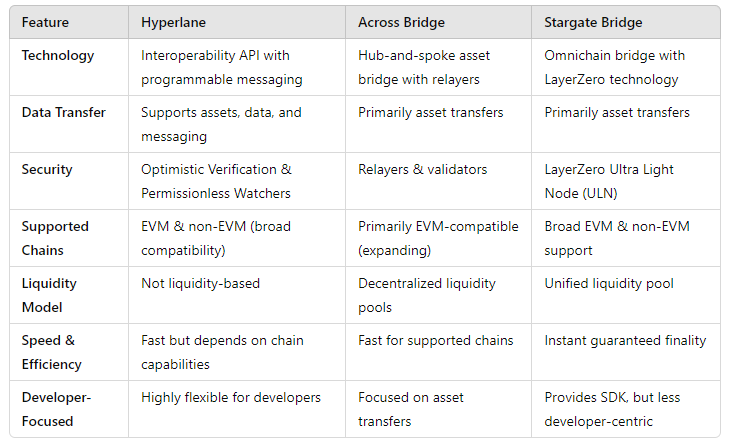
Let’s explore how Hyperlane stands against Across Bridge and Stargate Bridge. All three protocols aim to enable cross-chain communication, but they differ in their architecture, technology, and functionality.
1. Underlying Technology & Approach:
Hyperlane:
- Described as an « Interoperability API » for blockchain communication, Hyperlane is focused on providing generalized messaging across blockchains.
- Unlike traditional bridges that primarily transfer assets, Hyperlane allows for any type of cross-chain data and logic to be executed, offering developers more flexibility in building cross-chain applications.
- Uses a « programmable interchain messaging » approach, allowing projects to create custom logic for how assets and data interact across chains.
Across Bridge:
- Primarily an asset bridge that uses a relayer system to facilitate asset transfers through a hub-and-spoke model.
- Aimed at being a fast and efficient bridge for transferring assets between EVM-compatible chains.
Stargate Bridge:
- Utilizes LayerZero’s technology for an omnichain experience, offering asset transfers with instant finality and a unified liquidity pool.
- Focused on being a highly efficient asset bridge with seamless cross-chain transfers.
2. Type of Data Transfer:
Hyperlane:
- Not limited to asset transfers; it supports any kind of data transfer between blockchains, making it extremely versatile for developers looking to build interchain applications.
- This can include moving tokens, executing cross-chain smart contracts, and transferring messages.
Across Bridge:
- Primarily designed for asset transfers, not general data transfer, which makes it more specialized but less versatile compared to Hyperlane.
Stargate Bridge:
- Like Across Bridge, it focuses on asset transfers, but it’s built to be more seamless and efficient due to its integration with LayerZero technology.
3. Security Mechanisms:
Hyperlane:
- Employs a modular security model with a Permissionless Watcher and Optimistic Verification system, which allows anyone to participate in ensuring the security of cross-chain transactions.
- The Optimistic Verification mechanism means that transactions are assumed valid unless proven otherwise, providing scalability while maintaining security.
Across Bridge:
- Relies on a network of relayers and validators to ensure transaction accuracy and security, which is simpler but heavily dependent on these parties’ reliability.
Stargate Bridge:
- Uses the LayerZero Ultra Light Node (ULN) for security, offering a highly secure and tamper-proof cross-chain communication method. It’s one of the most advanced in terms of ensuring transaction security and correctness.
4. Supported Chains:
Hyperlane:
- Aims to be compatible with a wide variety of chains, including both EVM-compatible and non-EVM chains. Its design is flexible enough to adapt to different blockchain ecosystems.
Across Bridge:
- Initially focused on EVM-compatible chains but gradually expanding. It may not yet support as many chains as Hyperlane or Stargate.
Stargate Bridge:
- Due to its integration with LayerZero, it supports a wide range of EVM and non-EVM chains and continues to expand its reach.
5. Liquidity Model:
Hyperlane:
- Doesn’t rely on a traditional liquidity model like the other two. Instead, it focuses on enabling communication across chains, which means liquidity provision is not a core part of its functionality.
Across Bridge:
- Uses a decentralized network of liquidity providers who lock assets in pools to facilitate transfers. The liquidity is spread across different chains.
Stargate Bridge:
- Employs a unified liquidity model, allowing for seamless asset transfers across different chains using a single liquidity pool.
6. Speed & Efficiency:
Hyperlane:
- Offers relatively fast communication and transaction processing across chains, but the speed can vary based on the verification process and the chain’s capabilities.
Across Bridge:
- Known for its efficiency and speed for asset transfers, making it an attractive choice for quick transactions.
Stargate Bridge:
- Provides instant guaranteed finality, ensuring rapid and efficient asset transfers with minimal waiting time.
7. Developer-Focused Features:
Hyperlane:
- Highly developer-friendly, offering an easy-to-integrate API for building cross-chain applications and smart contracts.
- Suitable for projects requiring complex cross-chain logic, messaging, and data transfer.
Across Bridge:
- Primarily focused on asset bridging, with fewer developer-oriented features for building complex cross-chain applications.
Stargate Bridge:
- While not as developer-centric as Hyperlane, it provides a solid SDK and tools for integrating omnichain transfers into dApps.
Summary:
Which One Should You Choose?
Hyperlane: Ideal for projects that require cross-chain communication, logic execution, and data transfer beyond simple asset bridging. It’s an excellent choice for developers building more complex cross-chain applications or DeFi protocols.
Across Bridge: Best suited for users who need fast, efficient, and cost-effective asset transfers across a smaller set of EVM-compatible chains. Its simplicity makes it accessible to users looking for straightforward bridging solutions.
Stargate Bridge: The go-to choice for seamless, omnichain asset transfers with instant finality. It’s perfect for users and developers needing efficient, secure, and broad cross-chain interoperability, especially for DeFi applications.
In summary, Hyperlane offers more flexibility and developer capabilities for cross-chain applications, while Across Bridge and Stargate Bridge are more specialized in efficient asset bridging with their respective advantages in speed, security, and liquidity management.


